Ear Candles: Exploring this Efficient Alternative Therapy
October 03, 2023In the hustle and bustle of modern life, stress has become an unwelcome companion for many. The constant flood of information, work demands, and social pressures have created an environment that can leave you feeling overwhelmed and exhausted. However, amid this chaos, a remarkable system within your body offers solace and restoration, i.e., the parasympathetic nervous system, commonly called the "rest and digest" system. It plays an important role in helping you unwind, recharge, and combat the adverse effects of stress.
Continue reading to know the intricate workings of the parasympathetic nervous system, explore its role in stress reduction, and uncover practical techniques to harness its power for a healthier, more balanced life.
The Basic Network of the Nervous System
When people think about the nervous system, they associate it primarily with the brain. However, the truth is that the nervous system as a whole is distributed throughout your body. Its primary purpose is to transmit and receive signals.
A type of nerve fibers known as afferent or axons carry signals from the body to the brain. These signals enable rapid information processing. On the other hand, efferent nerve fibers have the opposite role. They convey messages from the nervous system to activate muscles and glands in response to specific stimuli.
The nervous system has multiple branches, with two central control centers:
- Central Nervous System (CNS): This consists of the brain, brainstem, and spinal cord, functioning as the central control hub for all bodily activities.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): The peripheral nerve system, which covers the entire body, is divided into two major groups.:
- The Somatic Nervous System
The somatic nervous system also has another name, the voluntary nervous system. This part handles sensations and nerve signals related to voluntary movements1. Examples of these movements include walking, hugging, and self-initiated motions.
- The Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system is commonly known as the involuntary nervous system. This branch regulates all nerve-related functions that operate beyond your conscious control and may go unnoticed. These functions include breathing, heart rate, digestion, urination, and more2.
Branches of Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system further splits into two more branches, given below.
The Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) helps your body respond to challenges with a "fight-or-flight" reaction. It releases chemicals like norepinephrine, epinephrine, and other messengers3.
Cortisol, a hormone from your adrenal glands, is also important for SNS. It affects things like making blood vessels narrower. It also controls your immunity and is a big part of inflammation. Cortisol can weaken inflammation depending on what's happening, like when germs or stress are involved. When you consistently face stressors, the sympathetic nervous system can become overly active, leading to a constant state of fight-or-flight response4. This prolonged activation can give rise to various health issues, like weakened immune systems, high blood pressure, and even conditions like anxiety disorders.
The Parasympathetic Nervous system
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is the other branch of the autonomic nervous system. The vagus nerve is at the core of the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS), which makes up about 75% of this system. The vagus nerve, sometimes known as the tenth cranial nerve, is a large neural tract that starts in the brainstem and goes down to the abdomen5. It intricately interacts with vital organs like the heart, lungs, and digestive system, regulating various body functions.
Working harmoniously, the vagus nerve and the PSNS contribute to processes recognized as the "rest and digest" response, facilitating the restoration of equilibrium within the body. The PSNS plays a role in relaxing your cardiovascular system through actions like widening blood vessels. This sharply contrasts the sympathetic nervous system's influence on blood vessels. Furthermore, the PSNS also influences your respiratory health.
Through intricate connections formed by ganglions and neurons, the parasympathetic system establishes a comprehensive network that reaches every organ in the body. This close interaction prompts the PSNS to function as an early warning system for the body, capable of detecting even subtle shifts linked to exposure to detrimental agents and other inflammatory responses6.
Enteric Nervous System
The enteric nervous system is an additional crucial branch of the nervous system's framework. It is a complex network of nerves that resides within the walls of the gastrointestinal tract, often referred to as the "second brain" due to its independent control over digestion and gut functions. The enteric nervous system, which comprises many neurons, is responsible for various functions within the digestive system. These encompass the movement of food, the secretion of digestive enzymes, and communication with the central nervous system7. This intricate neural network empowers the enteric nervous system to swiftly respond to shifts in the gut environment, enabling it to coordinate digestion and nutrient absorption efficiently. As a result, the enteric nervous system plays a major role in promoting optimal digestive health and overall well-being.
Parasympathetic Nervous System's Role in Stress
The parasympathetic nervous system's impact on stress is facilitated by neurotransmitters like acetylcholine and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Acetylcholine promotes relaxation and has an important role in the parasympathetic response, while GABA, renowned for its calming effects, helps manage anxiety and stress by inhibiting excessive neuronal activity.
The activation of the parasympathetic system not only relies on neurotransmitters but also involves various physiological pathways. It often leads to a decrease in heart rate and the relaxation of blood vessels, contributing to an overall sense of calmness. This system also influences digestion, enhancing nutrient absorption and energy conservation.
One vital player in the parasympathetic stress response is the vagus nerve. Stimulation of the vagus nerve, known as vagal tone, correlates with higher heart rate variability—a marker of the body's capacity to adapt to stressors. Those with elevated vagal tone tend to display greater resilience to stress and improved emotional regulation. The parasympathetic nervous system significantly contributes to managing anxiety and promoting emotional well-being through these intricate mechanisms.
Effects of Parasympathetic Nervous System Imbalance
An imbalance in the parasympathetic nervous system can have notable effects, particularly on stress. When this branch of the autonomic nervous system is disrupted, it can lead to difficulties achieving a state of relaxation and calmness. The parasympathetic system's role in promoting rest and recovery becomes compromised, making it harder for the body to counteract the effects of chronic stress8. This imbalance might result in heightened stress levels, impaired emotional regulation, and an increased susceptibility to anxiety-related disorders.
Furthermore, disturbances in parasympathetic function can impact other physiological processes, potentially contributing to digestive issues, cardiovascular problems, and a weakened immune system. An imbalanced parasympathetic nervous system can significantly influence an individual's well-being and stress management capabilities.
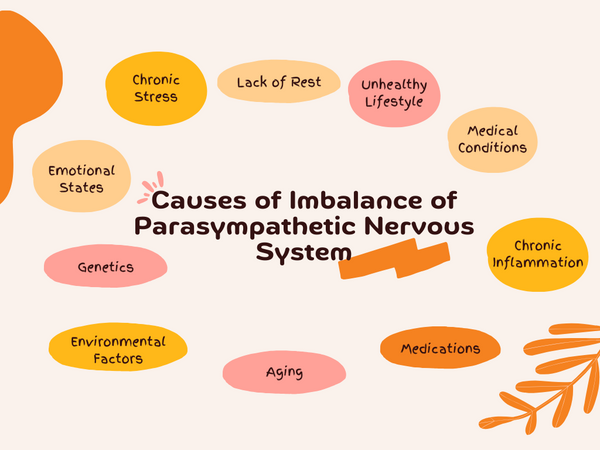
Causes of Imbalance of Parasympathetic Nervous System

Various factors can upset the balance of the parasympathetic nervous system, affecting how your body responds to stress. Knowing these causes can help you maintain your body's natural balance. Here are some main reasons for parasympathetic imbalance:
- Chronic Stress: Prolonged stress can over-activate the sympathetic nervous system, disrupting the balance with the parasympathetic system.
- Lack of Rest: Insufficient rest and sleep affect the parasympathetic system's ability to recover.
- Unhealthy Lifestyle: Lack of exercise, improper diet, and excessive stimulants impact the parasympathetic function.
- Medical Conditions: Health issues like neuropathy or heart problems can disturb parasympathetic regulation.
- Chronic Inflammation: Ongoing inflammation from poor diet and stress affects the parasympathetic system.
- Medications: Certain drugs, especially those affecting heart rate or neurotransmitters, influence the parasympathetic balance.
- Emotional States: Chronic anxiety or depression can affect the parasympathetic's stress regulation.
- Aging: The parasympathetic nervous system may become less efficient with aging, resulting in stress imbalances.
- Environmental Factors: Toxins and pollutants can interfere with the proper functioning the parasympathetic system.
- Genetic Factors: Some people might be genetically prone to parasympathetic imbalances.
Techniques for Supporting Parasympathetic Nervous System
By adopting specific techniques and practices, you can create an environment that fosters the balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. Here are effective techniques to support the parasympathetic nervous system:
Deep Breathing Exercises
Slow, deep breaths activate the vagus nerve, promoting parasympathetic activity. This natural response helps you relax, which lowers your stress level and makes you feel calmer. Studies show that incorporating these techniques into your routine can provide a valuable tool for managing everyday stress and promoting overall well-being9.
Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness practices like meditation, yoga, and tai chi effectively support the parasympathetic nervous system. Mindfulness meditation includes focusing on the present moment and practicing controlled breathing, reducing stress levels and enhancing parasympathetic response. Yoga combines breath, movement, and mindfulness, inducing relaxation and increasing flexibility. Also, the slow, deliberate moves of tai chi help balance the body and mind, which helps reduce stress.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation
Progressive muscle relaxation is a method to reduce physical stress and become more aware of the present moment. By carefully tightening and relaxing different muscle groups, people become more aware of how their bodies feel and learn to spot places where tension is building up. This practice helps the body relax and brings the mind and body closer together. By paying attention to the feelings in your muscles, you can become more aware of your body, lower overall muscle tension, and help yourself feel calm. Progressive muscle relaxation is a good way to deal with stress and mentally and physically relax. It can be a part of your daily practice.
Digital Detox
Reduce the time you spend in front of a screen and unplug from electronic devices on purpose. By taking a break from the steady flow of digital information, you can make room for mindfulness and stop being too stimulated. This break allows you to focus more on the present, letting the parasympathetic nervous system take over and helping you find a better balance between using technology and relaxing.
Creating Calming Environments for Relaxation
To make a place feel calm, choose soothing colors, add cozy furniture, and add things from nature, like plants or natural lighting. These style choices work together to create a sense of calm and ease, which makes it easier to relax. By surrounding yourself with a calm environment, you can make a haven that helps you relax, feel refreshed, and have a more parasympathetic-oriented atmosphere.
Meaningful Connections
Maintaining good relationships brings emotional support, creating a feeling of safety that triggers the calming parasympathetic nervous system. These connections play a big role in helping you relax and feel better. Studies show that spending time with friends and having meaningful conversations also help activate this calming response, making you feel more at ease and better able to handle stress 10.
Use of Ear Candles
Using ear candles can greatly enhance relaxation and influence the parasympathetic nervous system through a multi-sensory experience. This sensory stimulation, combined with the soft crackling sound of the candle, may have a calming effect, encouraging a state of relaxation.
You can further explore the benefits of ear candling by using Harmony's Ear Candles, which offers a diverse range of lavender, eucalyptus, peppermint, rosemary, and sage varieties. Each type is crafted to provide a unique sensory experience that aligns with relaxation and potential parasympathetic support.
Harmony's Lavender Ear Candles: Lavender's soothing aroma is associated with relaxation and stress reduction. Using lavender ear candles may create a calming atmosphere that contributes to relaxation and supports the parasympathetic nervous system.
Harmony's Eucalyptus Ear Candles: Eucalyptus's invigorating scent can offer a refreshing and revitalizing experience. While not directly linked to parasympathetic activation, its rejuvenating effect might indirectly aid relaxation.
Harmony's Peppermint Ear Candles: Peppermint's minty freshness provides a refreshing sensation. It's more known for energizing properties contributing to relaxation through a refreshed mind.
Harmony's Rosemary Ear Candles: Rosemary's herbal aroma is often associated with clarity and mental focus. It affects the mental state and indirectly supports relaxation.
Harmony's Sage Ear Candles: Sage has been used for cleansing and purifying properties. While not a direct relaxation tool, the ceremonial aspect may create a peaceful ambiance.
The Bottom Line
Amid the modern life hustle, stress has become an unwavering companion. However, within you resides a valuable ally – the parasympathetic nervous system. Managed by vagus nerves, this system offers you comfort and relief from stress. It's part of the autonomic nervous system, which works and functions beyond your control. When this system is balanced, it helps you relax, aids in digestion, and supports your overall well-being. Yet, imbalances can lead to increased stress, emotional struggles, and health concerns. Factors like ongoing stress, insufficient rest, or an unhealthy lifestyle can disrupt this equilibrium. To nurture it, consider practices like deep breathing, mindfulness, and creating a peaceful environment. Using ear candles like those from Harmony can also help you relax and bring your system back into balance. Returning to your parasympathetic nervous system can help you live a calmer, healthier existence amid life's rush.

